Anders Aas
Forsker
Sammendrag
Cover crops enhance soil quality and organic matter stability, yet the mechanisms linking belowground inputs to persistent soil organic matter (SOM) remain unclear. This study examined the effects of diversified cover cropping in barley systems on root biomass, SOM fractions, soil structure, microbial activity, and yield in central Norway (63.9° N), three years post-implementation. Six treatments were tested: (1) Control (barley without NPK), (2) Biochar-Fertilizer (barley + NPK + 3 Mg ha⁻¹ biochar), (3) Monocrop (barley), (4) Ryegrass (barley + ryegrass), (5) Clover (barley + ryegrass + white/red clover), and (6) Chicory (barley + ryegrass + red clover + chicory + bird’s-foot trefoil). Ryegrass and Clover systems produced 28.65 g m-² more root biomass at 0–13 cm (p < 0.05) and, along with Monocrop, stored 2.2 Mg ha-¹ more mineral-associated organic matter (MAOM) carbon and 0.2 Mg ha-¹ more MAOM nitrogen at 0–20 cm than other treatments. The Chicory system improved soil structure and biology, with higher aggregate stability, lower bulk density, and greater microbial abundance. Barley yields remained consistent across treatments, suggesting that cover cropping and low biochar inputs do not reduce productivity. Strong correlations (p < 0.01) between root biomass and MAOM stocks highlight root development as a key driver of SOM stabilization via organo-mineral associations. These findings underscore the role of root-enhancing cover crops in promoting MAOM formation and long-term SOM persistence, offering valuable insights for sustainable soil management.
Sammendrag
Abstract Background and Aims Efficient phosphorus (P) and management is essential for sustainable arable systems. Cover crops (CCs) are promising, but their performance is uncertain in high-latitudes. This three-year study evaluated CCs’ effects on P dynamics in a P-rich soil undersown in barley in Mid-Norway (63.9°N)—one of the northernmost trials of its kind. Methods A randomized complete block design included three CC treatments: ryegrass (CC1), a ryegrass–clover mix (CC2), and a four species mix including grass, legumes and herbs (CC3), and controls without CC (with/without NPK fertilizer). Soil and plant analyses included total and available P, total N, potentially mineralizable N (PMN), pH, permanganate-oxidizable carbon, root biomass, plant P concentrations, and microbial abundance via qPCR. Statistical analysis was based on Linear Mixed Models (LMMs). Results Cover crops successfully established (average biomass: 1525 kg ha⁻ 1 ), accumulated ~ 7 kg P ha⁻ 1 , and did not reduce barley yields. LMMs showed significant effects of CC treatment on root biomass, total P, and bacteria. Pairwise comparisons also revealed that fungal abundances in CC1 and CC3 were significantly higher than in the unfertilized control. Pairwise regression revealed that soil total P was strongly predicted by root biomass (β = 1.37, P < 0.001). Available P was negatively controlled by microbial pools (Bacteria: β = -9.22, P < 0.001) and residue quality (C:P ratio: β = -0.36, P < 0.001). Conclusions CCs can be used at 63°N without yield penalty. The primary P mechanism is mass-driven sequestration (root biomass) into the stable total P pool. However, P availability is temporally constrained by residue quality and microbial competition. Graphical Abstract
Forfattere
Christophe Moni Eva Farkas Claire Coutris Hanna Marika Silvennoinen Anders Aas Marit Almvik Liang Wang Kathinka Lang Liu Xingang Marianne StenrødSammendrag
Biochar and pesticides are likely to be increasingly used in combination in agricultural soils, yet their combined effects on climate change mitigation remain unexplored. This study presents an 8-month incubation experiment with different soil types (silt loam and sandy loam), biochars (corncob and corn stem), and pesticides (with and without a pesticide mixture), during which CO2 production from soil organic matter (SOM) and biochar mineralisation was monitored using isotopic methods. A comprehensive modelling approach, describing all mineralisation results over the entire incubation with a reduced set of parameters, was employed to isolate the effects of biochar, pesticides, and their interactions across soil types and carbon pools, and captured the dynamic effect of biochar on SOM mineralisation. Over 99.5% of biochars remained inert after 8 months, confirming the role of biochar as a carbon sequestration technology. Biochar addition showed higher SOM stabilisation potential in soil with high clay content compared to soil with low clay content. This suggests that biochar amendment should be considered carefully in clay-depleted soils, as it could result in a loss of native SOM. Corn stem biochar, characterised by high surface area and low C/N ratio, demonstrated higher SOM stabilisation potential than corncob biochar with low surface area and high C/N ratio. Pesticide application reduced SOM mineralisation by 10% regardless of soil and biochar types. Finally, the interaction between corncob biochar and pesticides further reduced SOM mineralisation by 5%, while no interactive effect was observed with corn stem biochar. These findings highlight the importance of considering biochar-pesticide interactions when evaluating the impact of biochar amendments on native SOM stability.
Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
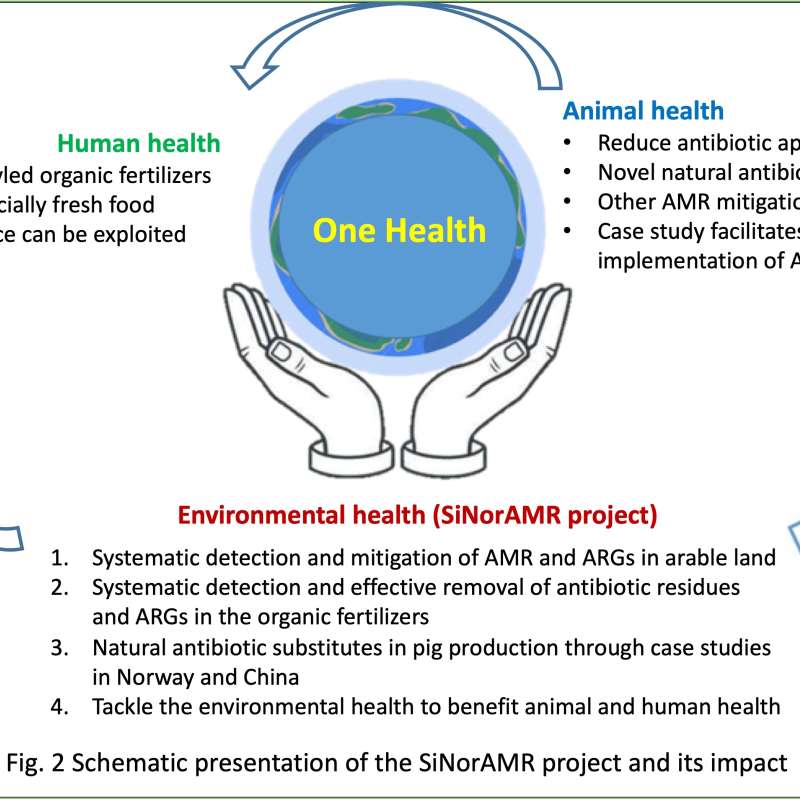
SiNorAMR
Full title: Collaborative and Knowledge-building Project Collaborative Project Systematic detection and mitigation of antimicrobial resistance in soil environment and animal health contributing to human health (SiNorAMR)
Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
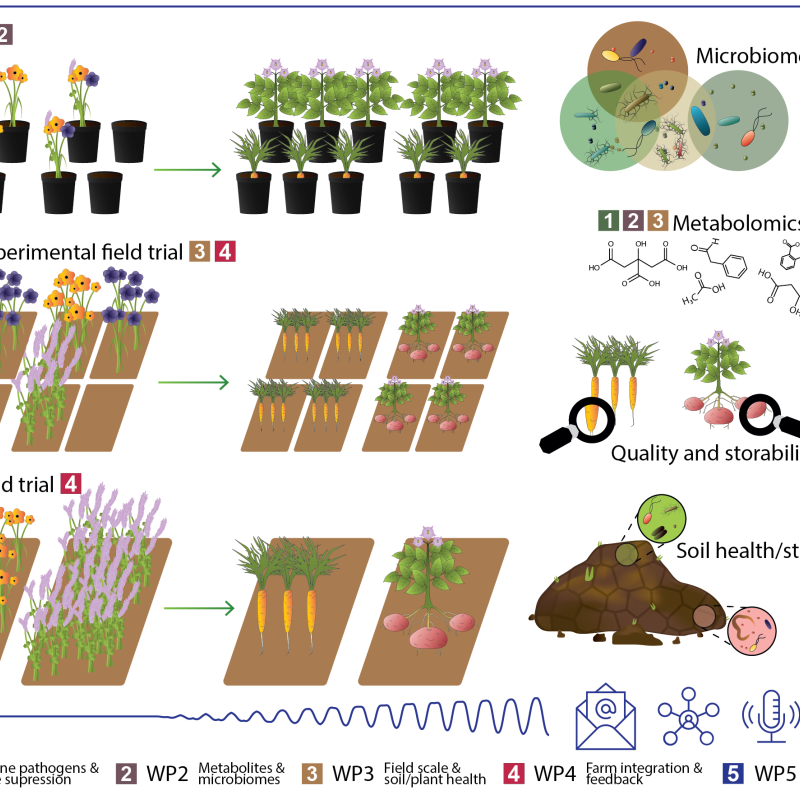
Cropdrive
Cropdrive aims to identify a selection of cover crops suitable for use in root vegetable and potato production with beneficial impacts on both soil and plant health, and greenhouse gas exchange.
