Anne-Grete Roer Hjelkrem
Forsker
(+47) 971 18 993
anne-grete.hjelkrem@nibio.no
Sted
Ås - Bygg H7
Besøksadresse
Høgskoleveien 7, 1433 Ås
Vedlegg
CV (januar 2025)Biografi
- Utvikling av varslingsmodeller for beslutningsstøtte innen soppsykdommer, toksiner, skadedyr og ugras
- Utvikling av NORNE-modellen for beregning av avling og kvalitet i grovfôr
- Utvikling av modelleringsplattform for beregning av klimagassutslipp i jordbruket i tråd med det nasjonale utslippsregnskapet
- Utvikling av modelleringsplattform for beregning av referansebaner og tiltaksscenarioer i oppdrag
- Miljøanalyser (LCA) innen matproduksjon
Sammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Sammendrag
Beitebruk er viktig for ressursutnyttelse, selvforsyning, dyrevelferd og kulturlandskap, og det er et politisk mål å øke beiting. Klimaeffektene av beiting har imidlertid vært lite vektlagt. Rapporten sammenstiller kunnskap om hvordan beitedyr påvirker klima gjennom både klimagassutslipp og endringer i vegetasjon og areal. Effektene varierer betydelig mellom arealtyper, beitetrykk, dyreslag og lokale forhold, noe som gjør det vanskelig å trekke generelle konklusjoner. I klimagassregnskapet er beiting særlig relevant for arealbruksendringer, som avskoging til beite og utslipp fra tidligere drenert myr. Effekter på enterisk metan og utslipp fra husdyrgjødsel er relativt små, selv om enkelte norske studier antyder noe lavere metanutslipp ved godt beite på fulldyrka jord. Biogeofysiske effekter som albedo er lite kartlagt, men kan ha nedkjølende effekt i noen områder. Rapporten peker på to hovedutfordringer: behov for sterkere insentiver til å bruke eksisterende innmarksbeiter fremfor nyrydding, og potensial for mer beiting av melkekyr på fulldyrka jord. Det trengs mer forskning for å bedre beregne effekter av beiting i klimagassregnskapet, særlig knyttet til enterisk metan, jordkarbon og beitetrykk i utmark.
Sammendrag
Disease symptoms, sources of inoculum, and patterns of spore release of Mycosphaerella ribis, the cause of Mycosphaerella leaf spot, were studied over three years in an organic blackcurrant planting receiving no fungicide applications. In addition to typical foliar symptoms, also fruit lesions were observed on the cultivars included in the study. Ascospores from leaf litter on the ground were trapped from bud break in April to mid-to-late July, but 99% were released by one month before. Conidia formed in old fruit cluster stalks overwintering on the blackcurrant shrubs were present from bud break to early August, but 99% were trapped from late May to mid-July. Conidia were found in leaf litter but were never captured in the spore trap, and ascospores were observed in old fruit cluster stalks. Degree-day models (base = 0˚C) were used to estimate the proportion of mature spores. Extended periods of dry conditions slowed spore maturation in the field. Models halting degree-day accumulation after 4 or 7 days with no rain (< 0.2 mm) or leaf wetness of < 12 h per day, gave the best performance for release of conidia or ascospores, respectively, if validated by data from controlled conditions in the laboratory. Ascospore release was suppressed during night, and if rain and wetness started during night and continued the following day, very few spores were released before sunrise. The present investigation provides new information that may be used when planning sanitary measures to reduce primary inoculum and predict spore release patterns for Mycosphaerella leaf spot.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
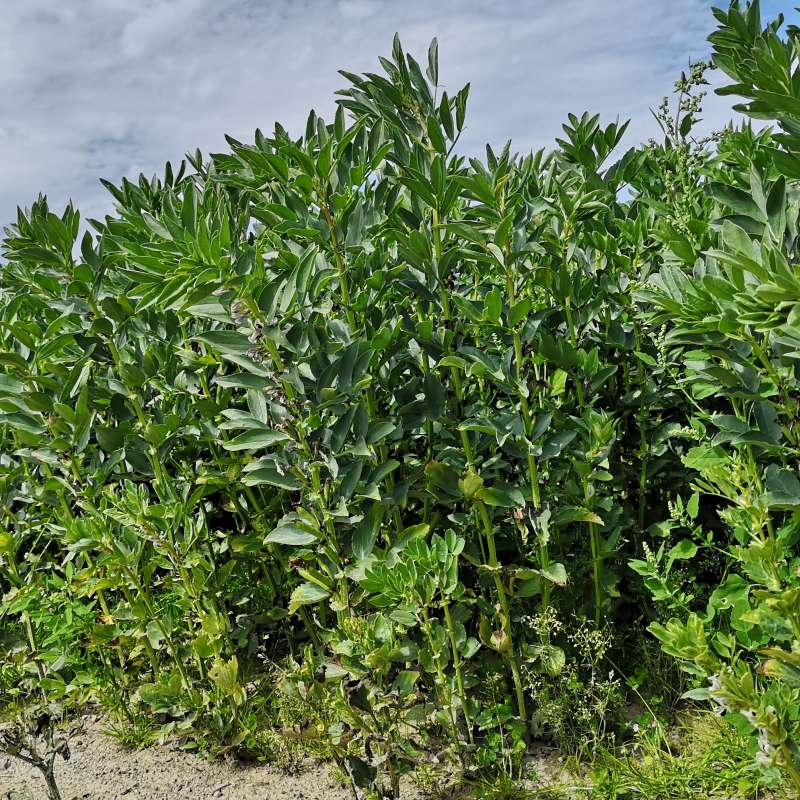
FABANOVA- Climate ready faba beans for the Nordic and Baltic region
The project will lead to improved faba bean lines and knowledge that can lead to higher and more stable protein yields in our challenging environment. NIBIO will develop forecasting tools for chocolate spot epidemics, enabling farmers to protect their crops.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
FABANOVA - Klimatilpassa åkerbønner for Norden og Baltikum
Prosjektet vil føre til bedre sorter og foredlingslinjer av åkerbønner og gi kunnskap som kan bidra til høyere og mer stabile planteprotein-avlinger i et stadig mer utfordrende klima. NIBIO skal starte utviklingen av varslingstjenester for sjokoladeflekk der målet er å kunne hjelpe produsenter til mer effektiv sjukdomsbekjempelse.
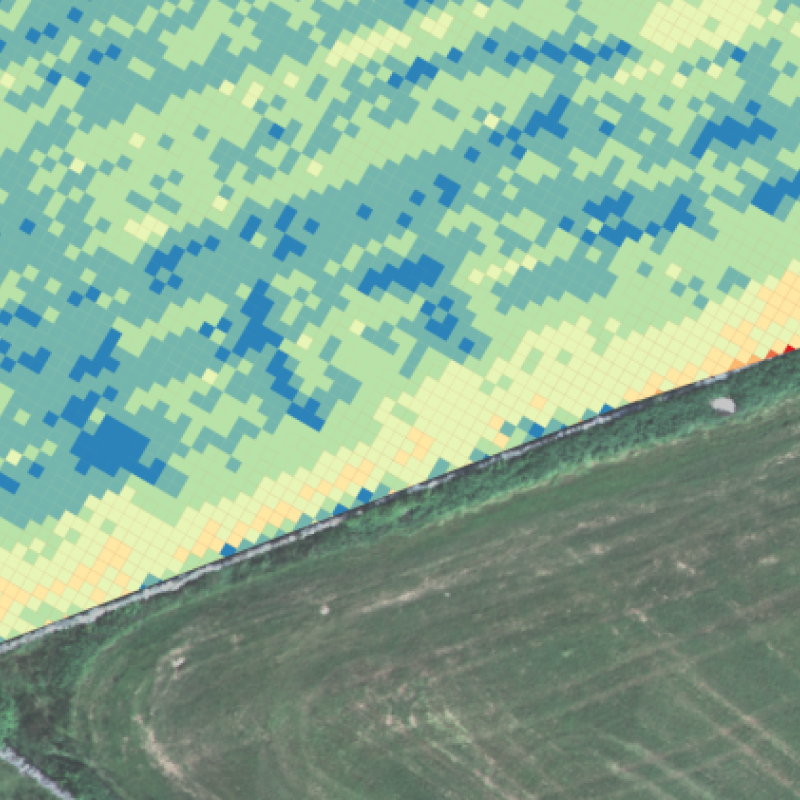
Divisjon for matproduksjon og samfunn
COPERNICUS - Jordbruk
Formålet med prosjektet er å ta i bruk satellitt-data fra Copernicus programmet for å utvikle rutiner og verktøy rettet inn mot jordbruksfaglige problemstillinger, og gjennom dette bidra med informasjon og råd til relevante aktører (bønder, rådgivere, jordbruksnæringa, kommuner, politikere og utdanningsinstitusjoner). Prosjektet skal dermed bidra til å forbedre dagens dyrkningspraksis, som gjennom en bedre utnyttelse av innsatsfaktorer som gjødsel og fôr også bidrar til å redusere klimaavtrykket til det norske jordbruket.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
Kunnskap om faktorer som påvirker utvikling av sopp og soppgifter
Prosjektet skal identifisere faktorer som påvirker innhold av soppgifter eller andre naturlig dannede uønskede stoffer i planter, og utvikle kunnskap som kan bidra til å redusere forekomsten av slike gifter.

Divisjon for bioteknologi og plantehelse
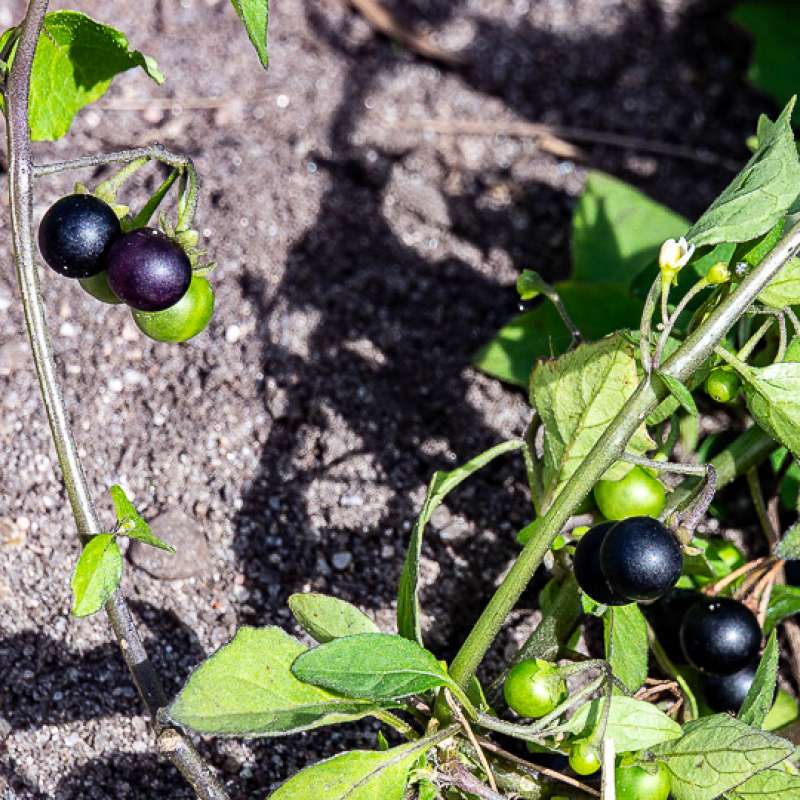
SOLWeeds: Effektiv bekjemping av svartsøtvier og begersøtvier i grønnsaker og potet
Svartsøtvier (Solanum nigrum L.) og begersøtvier (S. physalifolium Rusby) er ugras som forårsaker store problemer for norske produsenter av grønnsaker og potet. Flere dyrkere mener at problemet og lukekostnadene er så store at de frykter de må redusere dyrka areal av f.eks. gulrot, eller stoppe produksjonen helt. I potet er spesielt tidligproduksjonen under dekke utsatt.

