Hege Særvold Steen
Senioringeniør
(+47) 404 82 914
hege.sarvold.steen@nibio.no
Sted
Ås - Bygg H7
Besøksadresse
Høgskoleveien 7, 1433 Ås
Forfattere
Iuliana Caras Irina-Elena Ionescu Ana-Maria Pantazica Andre van Eerde Hege Særvold Steen Inger Heldal Sissel Haugslien Catalin Tucureanu Raluca-Elena Chelmus Vlad-Constantin Tofan Adriana Costache Adrian Onu Hang Su Norica Branza-Nichita Jihong Liu Clarke Crina StavaruSammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Forfattere
Ana-Maria Madalina Pantazica Andre van Eerde Mihaela-Olivia Dobrica Iuliana Caras Irina Ionescu Adriana Costache Catalin Tucureanu Hege Særvold Steen Catalin Lazar Inger Heldal Sissel Haugslien Adrian Onu Crina Stavaru Norica Branza-Nichita Jihong Liu ClarkeSammendrag
The recent SARS-CoV-2 pandemic has taught the world a costly lesson about the devastating consequences of viral disease outbreaks but also, the remarkable impact of vaccination in limiting life and economic losses. Vaccination against human Hepatitis B Virus (HBV), a major human pathogen affecting 290 million people worldwide, remains a key action towards viral hepatitis elimination by 2030. To meet this goal, the development of improved HBV antigens is critical to overcome non-responsiveness to standard vaccines based on the yeast-produced, small (S) envelope protein. We have recently shown that combining relevant immunogenic determinants of S and large (L) HBV proteins in chimeric antigens markedly enhances the anti-HBV immune response. However, the demand for cost-efficient, high-quality antigens remains challenging. This issue could be addressed by using plants as versatile and rapidly scalable protein production platforms. Moreover, the recent generation of plants lacking β-1,2-xylosyltransferase and α-1,3-fucosyltransferase activities (FX-KO), by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing, enables production of proteins with “humanized” N-glycosylation. In this study, we investigated the impact of plant N-glycosylation on the immunogenic properties of a chimeric HBV S/L vaccine candidate produced in wild-type and FX-KO Nicotiana benthamiana. Prevention of β-1,2-xylose and α-1,3-fucose attachment to the HBV antigen significantly increased the immune response in mice, as compared with the wild-type plant-produced counterpart. Notably, the antibodies triggered by the FX-KO-made antigen neutralized more efficiently both wild-type HBV and a clinically relevant vaccine escape mutant. Our study validates in premiere the glyco-engineered Nicotiana benthamiana as a substantially improved host for plant production of glycoprotein vaccines.
Forfattere
Hang Su Andre van Eerde Hege Særvold Steen Inger Heldal Sissel Haugslien Irene Ørpetveit Stefanie Caroline Wüstner Makoto Inami Marie Løvoll Espen Rimstad Jihong Liu ClarkeSammendrag
Det er ikke registrert sammendrag
Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
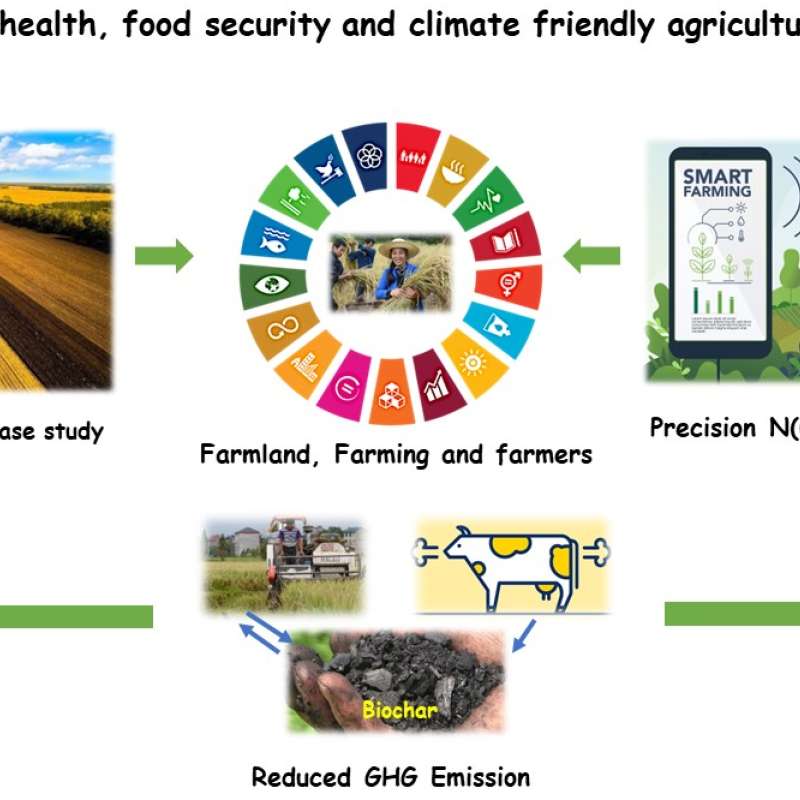
Sinograin III: Smart agricultural technology and waste-made biochar for food security, reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission, and bio-and circular economy
The Sinograin III project’s overall objective is to contribute to the UN SDGs by widely implementing precision agriculture technologies and application of “waste-to-value” biochar products to achieve sustainable food production with minimized GHG emission, improve soil fertility and promote green growth/zero waste in modern agriculture in China.
Divisjon for miljø og naturressurser
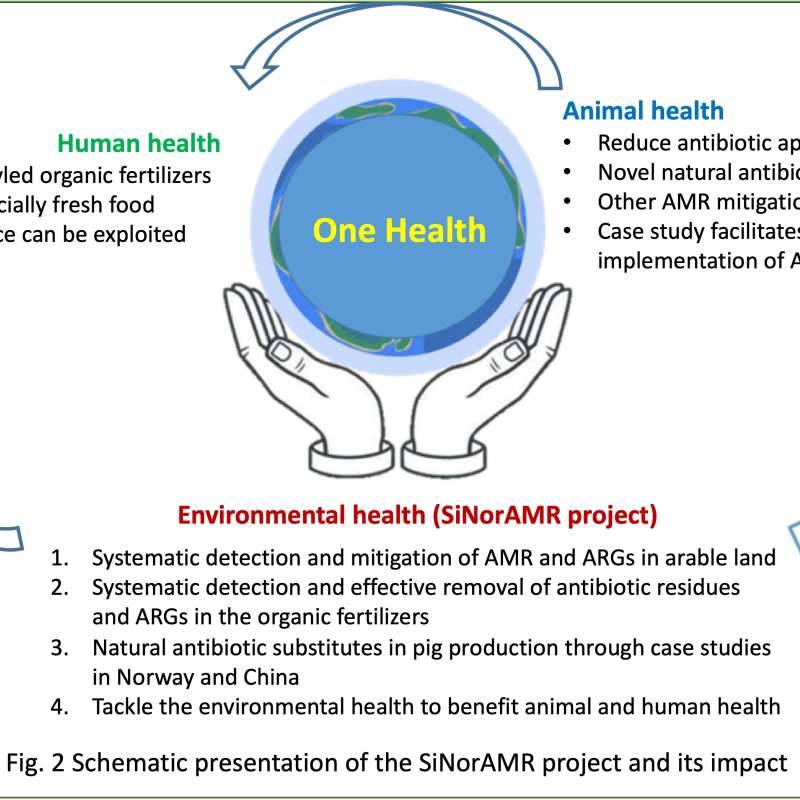
SiNorAMR
Full title: Collaborative and Knowledge-building Project Collaborative Project Systematic detection and mitigation of antimicrobial resistance in soil environment and animal health contributing to human health (SiNorAMR)
