Thiago Inagaki
Research Scientist
Biography
Bachelor's and Master's in Agronomy and a Dr. in Natural Sciences (Dr. rer. nat.) focusing on Soil Science. Research focused on the effects of land use and management on soil C persistence, and mechanisms of soil organic matter protection through organo-mineral associations. Led projects intersecting soil quality, sustainability, and geosciences using advanced methods, including 13C-NMR, SEM/TEM, STXM, NanoSIMS, FIB-SEM, and stable isotopes (13C and 15N).
Authors
Aline Roma Tomaz Rattan Lal William Ramos da Silva Thiago Inagaki Aline dos Santos Correia Felipe José Cury Fracetto Giselle Gomes Monteiro Fracetto Clever Briedis Débora Marcondes Bastos Pereira Milori Abelardo Antônio de Assunção Montenegro Ademir de Oliveira FerreiraAbstract
In semiarid regions, soil organic carbon (SOC) stocks and soil organic matter (SOM) pools are often low due to limited biomass input and inadequate management. This study evaluated SOC stocks and SOM fractions in a forage cactus–sorghum intercropping system irrigated with treated sewage water under diverse mulch in the northeastern Brazilian semiarid. The experiment followed a randomized split-plot block design with four replicates. Main plots included four irrigation levels (0, 80, 100, and 120 % of sorghum evapotranspiration (ETc)), and split plots comprised two mulch treatments: no mulch (NM) and mulch (WM) with 8 Mg ha−1 of sabi grass, spiny burrgrass, and goosegrass. Soil samples were collected at 0–0.10, 0.10–0.20, and 0.20–0.40 m depths in three sorghum cuts to determine labile SOM fractions: hot water-extractable C (HWEO-C), potassium permanganate-oxidizable C (POX-C), and particulate organic C (POC). In addition, SOC stocks and humic substances (HS), including humin (HU), fulvic acid (FA), and humic acid (HA), were determined at the end of the experiment. Intercropping system productivity was also evaluated. The highest SOC, POC, POX-C, and HWEO-C stocks occurred in 80WM and 100WM treatments, especially in HS, with HU as the dominant component. SOC in the HU fraction exceeded that in native vegetation soils, with threefold increases at 0–0.10 m and six-to sevenfold increases in deeper layers. Soils without irrigation, regardless of mulch, exhibited lower C storage, underscoring the importance of water management. Combining reclaimed water irrigation and mulching enhanced SOC accumulation, particularly in stable humic fractions, boosted carbon sequestration and crop productivity, and fostered sustainable, climate-resilient agriculture in semiarid tropical regions.
Abstract
Cover crops enhance soil quality and organic matter stability, yet the mechanisms linking belowground inputs to persistent soil organic matter (SOM) remain unclear. This study examined the effects of diversified cover cropping in barley systems on root biomass, SOM fractions, soil structure, microbial activity, and yield in central Norway (63.9° N), three years post-implementation. Six treatments were tested: (1) Control (barley without NPK), (2) Biochar-Fertilizer (barley + NPK + 3 Mg ha⁻¹ biochar), (3) Monocrop (barley), (4) Ryegrass (barley + ryegrass), (5) Clover (barley + ryegrass + white/red clover), and (6) Chicory (barley + ryegrass + red clover + chicory + bird’s-foot trefoil). Ryegrass and Clover systems produced 28.65 g m-² more root biomass at 0–13 cm (p < 0.05) and, along with Monocrop, stored 2.2 Mg ha-¹ more mineral-associated organic matter (MAOM) carbon and 0.2 Mg ha-¹ more MAOM nitrogen at 0–20 cm than other treatments. The Chicory system improved soil structure and biology, with higher aggregate stability, lower bulk density, and greater microbial abundance. Barley yields remained consistent across treatments, suggesting that cover cropping and low biochar inputs do not reduce productivity. Strong correlations (p < 0.01) between root biomass and MAOM stocks highlight root development as a key driver of SOM stabilization via organo-mineral associations. These findings underscore the role of root-enhancing cover crops in promoting MAOM formation and long-term SOM persistence, offering valuable insights for sustainable soil management.
Authors
Caio Nunes Gonçalves Felipe José Cury Fracetto William Ramos da Silva Thiago Inagaki Renato Lemos dos Santos Giselle Gomes Monteiro Fracetto Ademir de Oliveira FerreiraAbstract
Sewage sludge-derived biochar, a carbon-rich material produced by the pyrolysis of sewage sludge, has emerged as a promising amendment for enhancing the fertility and biological quality of nutrient-poor sandy soils in tropical regions. We investigated the effects of sewage sludge (SS) and its biochar (SSB) on microbial indicators, nutrient dynamics, and sugarcane biomass growth in sandy soil over 120 days. Treatments included individual applications of SS (40 Mg ha−1) and SSB (20 Mg ha−1), their combinations at 75:25, 50:50, and 25:75 SS:SSB ratios, a mineral fertilizer, and an unfertilized control. Microbial biomass carbon (Cmic), basal C-CO2 flux, metabolic (qCO2) and microbial (qMic) quotients were monitored, along with ammonium and nitrate levels, available phosphorus (P), and carbon stock. SS promoted a rapid rise in microbial activity and Cmic, whereas SSB sustained these effects over time, demonstrating complementary roles. The 75:25 combination exhibited the strongest synergistic response, enhancing microbial efficiency (higher qMic and lower qCO2), P availability, and carbon storage. Ammonium and nitrate peaked during early and mid-stages, respectively, with the highest values under SS. At the same time, P availability and soil carbon stocks were maximized under 75:25. Sugarcane biomass increased significantly in this treatment, despite foliar N and P concentrations remaining below sufficiency levels. These results highlight clear synergistic interactions between SS and SSB, emphasizing that the 75:25 combination offers a balanced strategy to improve nutrient cycling, microbial functionality, and carbon stabilization in tropical sandy soils.

Division of Environment and Natural Resources
Conservation of Biodiversity in China in the light of Climate Change
Climate change is becoming an increasingly important pressure on biodiversity, which adds to the burden of other drivers of loss of biodiversity causing negative effects on ecosystems and species

Division of Environment and Natural Resources
AgriCascade
Cascading recycling of organic N-sources with next-generation biochar fertilizer for Norwegian agriculture
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
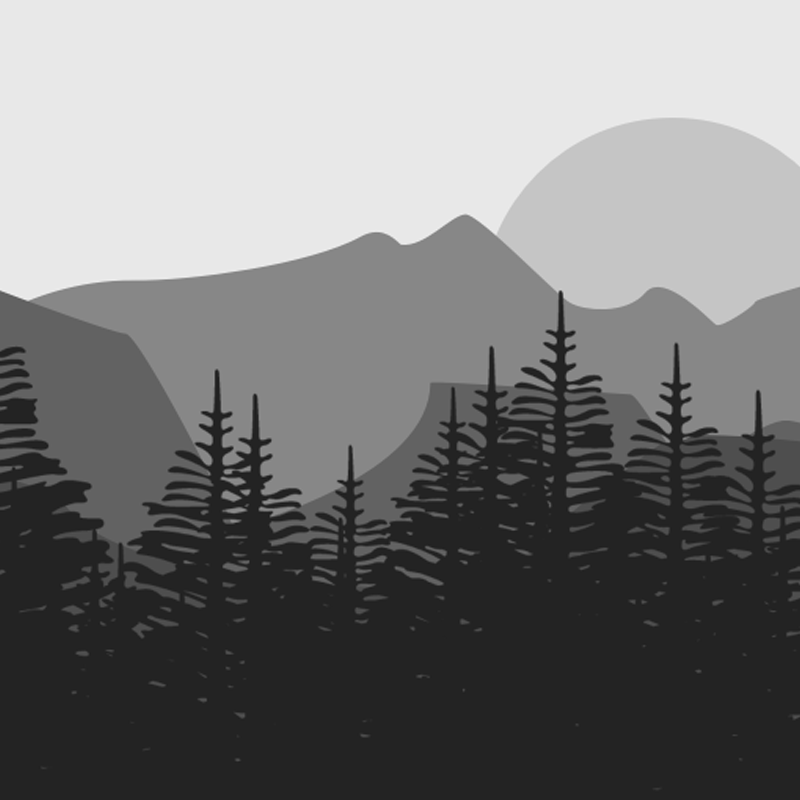
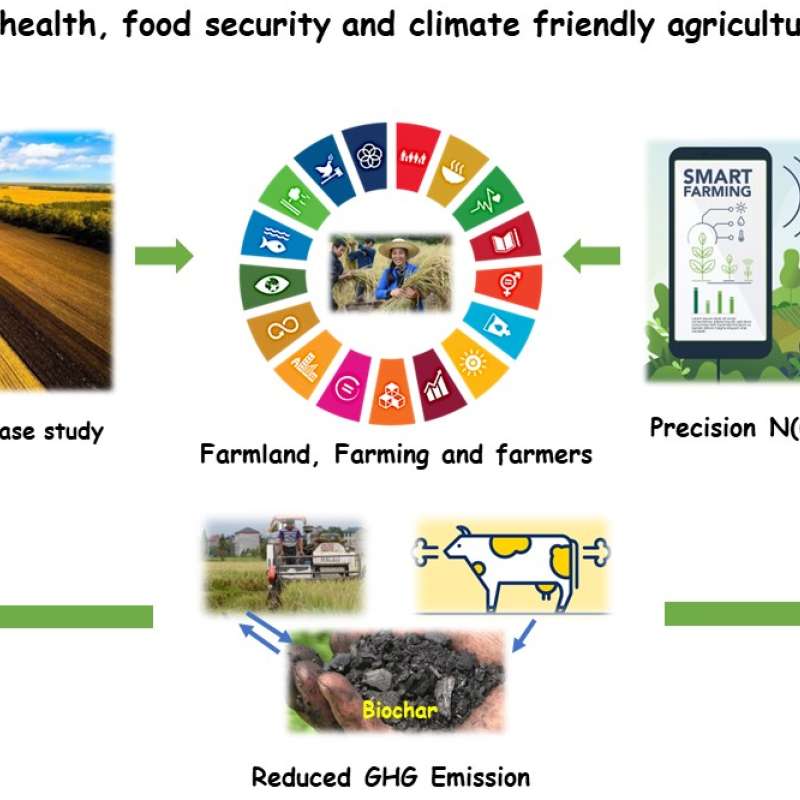
Sinograin III: Smart agricultural technology and waste-made biochar for food security, reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission, and bio-and circular economy
The Sinograin III project’s overall objective is to contribute to the UN SDGs by widely implementing precision agriculture technologies and application of “waste-to-value” biochar products to achieve sustainable food production with minimized GHG emission, improve soil fertility and promote green growth/zero waste in modern agriculture in China.
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
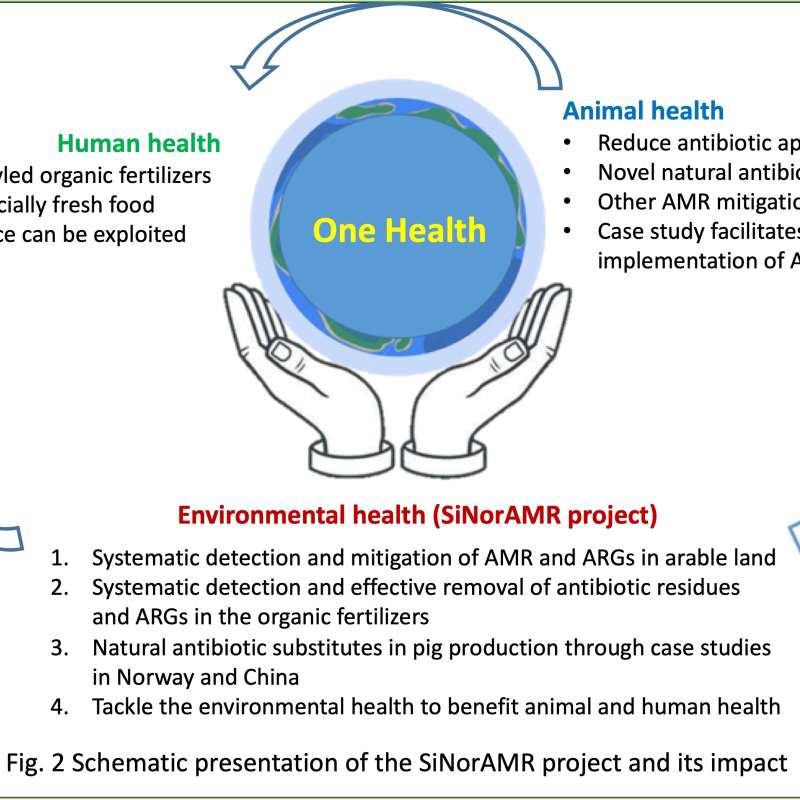
SiNorAMR
Full title: Collaborative and Knowledge-building Project Collaborative Project Systematic detection and mitigation of antimicrobial resistance in soil environment and animal health contributing to human health (SiNorAMR)
