Jihong Liu Clarke
Research Professor/Coordinator for China Relations
Authors
Igor A. Yakovlev Thiago Inagaki Junbin Zhao Pierre-Adrien Rivier Hege Særvold Steen Inger Heldal Daniel Rasse Jihong Liu Clarke Nicholas ClarkeAbstract
No abstract has been registered
Authors
Chi Wu Yuzhu Wang Jihong Liu Clarke Hang Su Liang Wang Olga A. Glazunova Konstantin V. Moiseenko Lan Zhang Liangang Mao Lizhen Zhu Xingang LiuAbstract
Owing to wide application and persistence, fluridone has demonstrated side-effects on non-target plants and aquatic organisms. This study investigated the potential of biochar as remediation in soil using rice hull biochar (BCR) produced at different temperatures and in four types of soil. The results indicated that, with increasing pyrolytic temperature from 300 to 700 ºC, biochar properties changed, for example, specific surface area values increased from 38.21 to 126.12 m2 g−1. Sorption affinity (Kf) of BCR ranged from 409 to 1352 and 1301 to 6666 (μg/g)/(mg/L)n for fluridone and its metabolite fluridone acid respectively. After amendment with 2% BCR500, fluridone and fluridone acid could easily be adsorbed in different types of soils, and Kf values were 1.30–3.73 times higher than those in pure soil. Half-lives values varied between different soils and fluridone acid (179–306 days) persisted significantly longer than fluridone (39–179 days) in soil. After amendment with 2% BCR500, fluridone and fluridone acid were degraded faster. Experiments under sterilized conditions demonstrated biodegradation to be the dominant process in unamended (61.59%–64.70%) and amended (67.71%–77.67%) soil. Bioinformatic analysis showed that fluridone reduced the diversity of the soil microbial community, but the abundance of microorganisms with degradation function increased and these became dominant species after BCR was added, particularly with higher numbers of degrading bacteria like Lysobacter, Pseudonocardia and Sphingomonas. Co-occurrences also revealed that BCR tightened bacterial connection and relieved fluridone stress. This work helps us better understand these processes and optimize the application of biochar for reducing pesticide contamination in agricultural soils.
Authors
Petter D. Jenssen Trond Mæhlum Melesse Eshetu_Moges Bente Føreid Trine Hvoslef-Eide Jihong Liu Clarke Arve Heistad Manoj Kumar PandeyAbstract
Urban agriculture requires resources such as growth media, nutrients, and water. This report demonstrates how these resources can be locally sourced through a circular economy approach, in which waste materials are recovered and reused. Recycling helps reduce or eliminate the discharge of pollutants into water and air. Examples presented show how to convert waste from households—such as human excreta, wastewater, and organic household waste—into biogas, compost/growth media, biochar, and solid and liquid fertilizer for urban agriculture and urban greening. The solutions presented have been explored through desktop evaluations, practical trials, or full-scale demonstrations to see how the technologies can be improved or adapted for urban use. Products like liquid and solid fertilizers, compost, aquaponic fish feed, irrigation water, and energy (methane) can be used in urban food production or recreational areas. Regulations for the use of waste resources in the production of growth media, fertilizers, irrigation water, fodder, and energy vary between countries but are generally restrictive due to the risk of disease transmission and pollutant build-up. For urban agriculture to become more circular, there is a need for documentation of good waste treatment routines, changes in legislation, and changes in attitudes towards the use of local waste resources.

Division of Environment and Natural Resources
Conservation of Biodiversity in China in the light of Climate Change
Climate change is becoming an increasingly important pressure on biodiversity, which adds to the burden of other drivers of loss of biodiversity causing negative effects on ecosystems and species
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
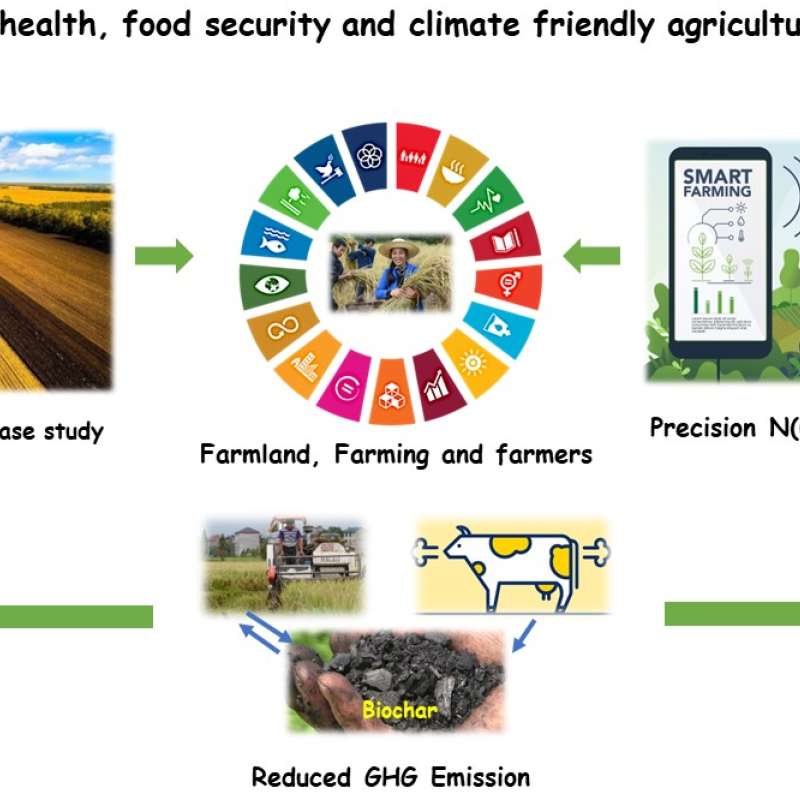
Sinograin III: Smart agricultural technology and waste-made biochar for food security, reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emission, and bio-and circular economy
The Sinograin III project’s overall objective is to contribute to the UN SDGs by widely implementing precision agriculture technologies and application of “waste-to-value” biochar products to achieve sustainable food production with minimized GHG emission, improve soil fertility and promote green growth/zero waste in modern agriculture in China.
Division of Environment and Natural Resources
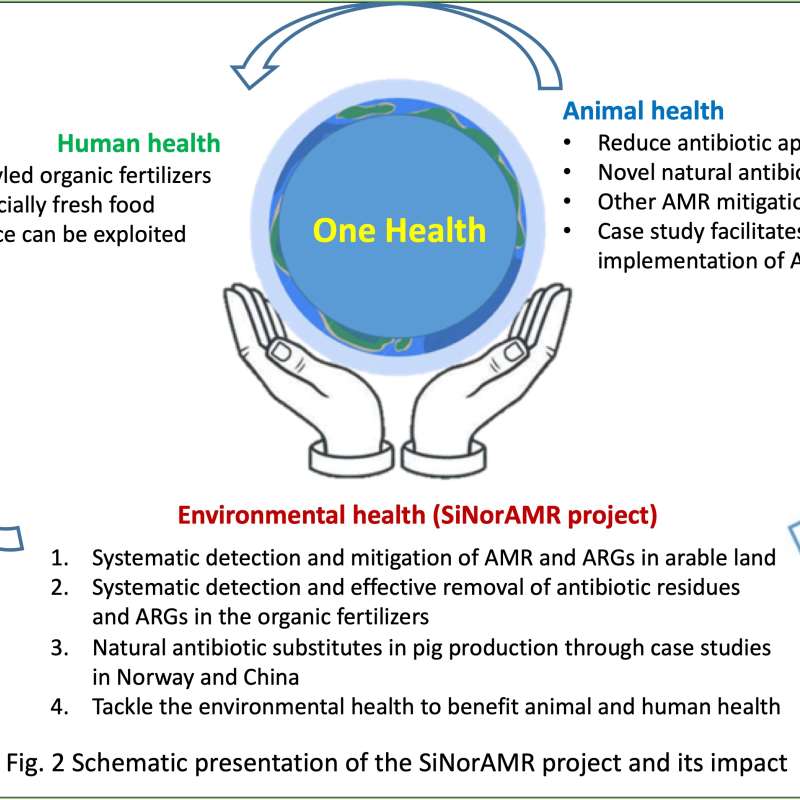
SiNorAMR
Full title: Collaborative and Knowledge-building Project Collaborative Project Systematic detection and mitigation of antimicrobial resistance in soil environment and animal health contributing to human health (SiNorAMR)
